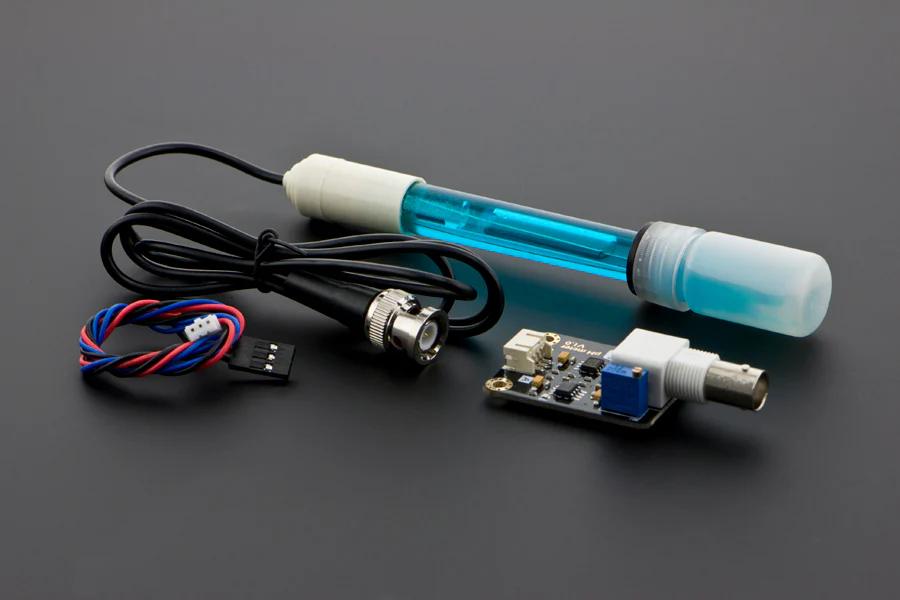
Agricultural activities are a major source of water pollution, as runoff from fields can carry fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals into nearby rivers, lakes, and groundwater. Monitoring the pH of water in these areas is essential to understand the impact of agricultural practices on water quality. A water pH sensor provides accurate, real-time measurements, enabling farmers, environmental managers, and researchers to detect and address runoff issues promptly.
Importance of pH Monitoring in Agricultural Runoff
The pH of water plays a crucial role in chemical reactions, nutrient availability, and the health of aquatic ecosystems. Excessive acidity or alkalinity can indicate contamination from fertilizers, lime, or other agricultural inputs. Regular monitoring of pH helps identify potential problems early, preventing damage to both the environment and human health.
A water ph sensor enables real-time monitoring of water bodies affected by agricultural runoff. By tracking changes in acidity or alkalinity, operators can implement mitigation strategies, such as adjusting fertilizer application, improving drainage systems, or installing buffer zones to protect sensitive ecosystems.
How a Water pH Sensor Works
Water pH sensors measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in water, translating it into a pH value that indicates acidity or alkalinity. The sensors typically consist of a measuring electrode and a reference electrode, which together produce an electrical signal that reflects the water’s pH.
Modern sensors are designed for field use, featuring temperature compensation, durable electrodes, and protective housings that ensure reliable measurements even in challenging outdoor conditions. Portable or automated setups allow for continuous or spot monitoring, depending on the needs of the study or operation.
Applications in Agricultural Monitoring
Monitoring agricultural runoff is essential for sustainable farming and environmental protection. Water pH sensors help identify areas where chemical inputs are affecting water quality, allowing for targeted interventions. This includes detecting runoff after heavy rainfall, identifying contamination from fertilizers or pesticides, and monitoring drainage from livestock operations.
Sensors can be deployed in rivers, streams, irrigation channels, or ponds to provide continuous data. These measurements help farmers make informed decisions about nutrient management, while regulators and researchers can use the data to assess the broader environmental impact of agricultural practices.
Supporting Environmental Protection
Agricultural runoff can lead to ecosystem degradation, including eutrophication, loss of biodiversity, and contamination of drinking water sources. By providing real-time pH measurements, water pH sensors allow early detection of harmful changes in water chemistry, enabling timely corrective actions.
This proactive approach helps protect aquatic life, maintain soil and water health, and ensure sustainable agricultural practices. It also supports regulatory compliance, as many regions require monitoring of water quality near agricultural lands.
Integration with Data Systems
Water pH sensors can be integrated with automated monitoring networks, enabling remote access, real-time alerts, and continuous data logging. This allows environmental managers and farmers to track trends over time and make data-driven decisions.
Cloud-based systems can store long-term data for analysis, helping to identify recurring issues, evaluate the effectiveness of mitigation measures, and support research on sustainable farming practices.
Ensuring Sensor Accuracy
For reliable monitoring of agricultural runoff, sensors must be regularly calibrated and maintained. Fouling from sediments, algae, or chemical residues can affect accuracy, and extreme temperatures or highly variable water chemistries may interfere with readings.
Routine cleaning, calibration with standard buffer solutions, and using sensors designed for field deployment ensure consistent and dependable performance. Selecting the right type of sensor for the water conditions and application is crucial for obtaining accurate data.
Conclusion
A water pH sensor is an essential tool for monitoring agricultural runoff, providing accurate and timely measurements of water acidity and alkalinity. By enabling early detection of contamination, supporting sustainable farming practices, and protecting ecosystems, these sensors contribute to responsible water management. Integration with automated systems, proper calibration, and careful maintenance ensure reliable long-term performance, helping farmers, environmental managers, and researchers make informed decisions for healthier waterways and more sustainable agriculture.